Data analytics

|
Analytics is a method which uses logical analysis to interpret large quantities of data to help with prediction and decision making. The analysis of data may include discerning trends and patterns, their interpretation and communication. Analytics is therefore the link between the data and making informed decisions. Organisations can use analytics to gain a predictive intelligence that can help shape their future plans.
Data used for analytics can be structured or unstructured. Structured data, for example, might be formatted into a table; whereas unstructured data cannot be tabulated e.g some documents or hearsay.
There are two main types of data:
- Descriptive data – this is data which describes things in the past e.g customer records, past performance, purchase history etc.
- Predictive data – this is closely linked to machine learning and looks at the future, and how to make predictions based on past events.
Once descriptive data has been gathered, it can be processed by algorithms (mathematical formulas or models) to create a model that identifies relationships in variables existing in the data and allows predictions to be made. Uncertain data for which the answers are not known e.g the type of goods that certain people in a geographical area might be interested in, can then be fed into the model which subsequently outputs what their preferences might be. This can then be reported or communicated in various formats such as tables, bar and line charts, etc.
The important result of the process is the creation of the model. Once established, data can be inputted to produce a prediction. This is the basis of machine learning which can lead to the attainment of artificial intelligence (AI).
Data analytics is useful in all walks of life but particularly in marketing where possible future consumer preferences can be predicted and therefore accommodated in campaigns. It can blend into performance analytics which may help a company measure its progress toward specific goals and to determine which actions will help achieve them.
Data analytics can be used for digital management to help construction firms to win projects and deliver them more efficiently. This is particularly apposite for large capital projects, for example, providing analysis to challenge trends in low-performance, getting a better understanding of project performance, root causes and prioritising daily activities.
Analytics will become increasingly important with the growth of big data, the internet of things and the use of sensors in the built environment.
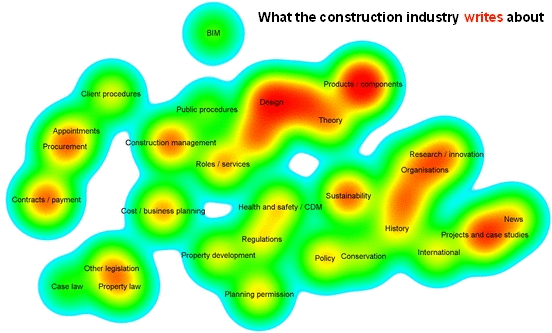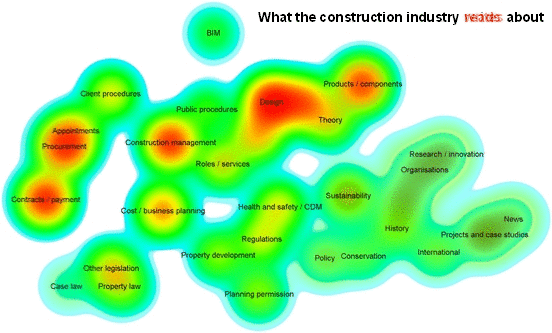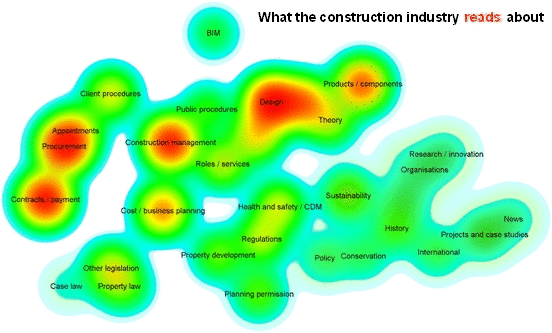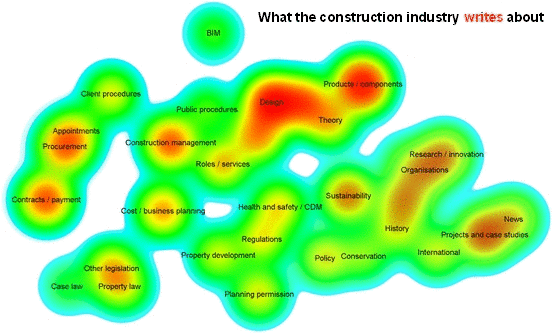
Analyics were used by Designing Buildings Wiki to assess the relationships between subjects on the website, and the difference between what authors write about and what users read about. For more information see: Fit for purpose - Big data reveals the construction knowledge gap
NB PwC Global, Digital procurement survey 2022, defines Data analytics as: ‘…the science of analyzing raw data to make conclusions about that information.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Asset information model.
- Big data.
- Building data exchange.
- Clustering.
- Common data environment.
- Data-centric business model.
- Data-driven mobility.
- Data and behaviours in construction.
- Data and infrastructure productivity.
- Data collection strategies.
- Data drop.
- Data manager.
- How data can stop waste.
- Interoperability.
- Internet of things.
- Making the most of big data.
- Open data - how can it aid the development of the construction industry?
- Predictive analytics.
- Procurement analytics.
- Top big data tools used to store and analyze data.
- Treating data as part of infrastructure
- Virtual reality and big data disrupting digital construction.
Featured articles and news
RTPI leader to become new CIOB Chief Executive Officer
Dr Victoria Hills MRTPI, FICE to take over after Caroline Gumble’s departure.
Social and affordable housing, a long term plan for delivery
The “Delivering a Decade of Renewal for Social and Affordable Housing” strategy sets out future path.
A change to adoptive architecture
Effects of global weather warming on architectural detailing, material choice and human interaction.
The proposed publicly owned and backed subsidiary of Homes England, to facilitate new homes.
How big is the problem and what can we do to mitigate the effects?
Overheating guidance and tools for building designers
A number of cool guides to help with the heat.
The UK's Modern Industrial Strategy: A 10 year plan
Previous consultation criticism, current key elements and general support with some persisting reservations.
Building Safety Regulator reforms
New roles, new staff and a new fast track service pave the way for a single construction regulator.
Architectural Technologist CPDs and Communications
CIAT CPD… and how you can do it!
Cooling centres and cool spaces
Managing extreme heat in cities by directing the public to places for heat stress relief and water sources.
Winter gardens: A brief history and warm variations
Extending the season with glass in different forms and terms.
Restoring Great Yarmouth's Winter Gardens
Transforming one of the least sustainable constructions imaginable.
Construction Skills Mission Board launch sector drive
Newly formed government and industry collaboration set strategy for recruiting an additional 100,000 construction workers a year.
New Architects Code comes into effect in September 2025
ARB Architects Code of Conduct and Practice available with ongoing consultation regarding guidance.
Welsh Skills Body (Medr) launches ambitious plan
The new skills body brings together funding and regulation of tertiary education and research for the devolved nation.
Paul Gandy FCIOB announced as next CIOB President
Former Tilbury Douglas CEO takes helm.
UK Infrastructure: A 10 Year Strategy. In brief with reactions
With the National Infrastructure and Service Transformation Authority (NISTA).